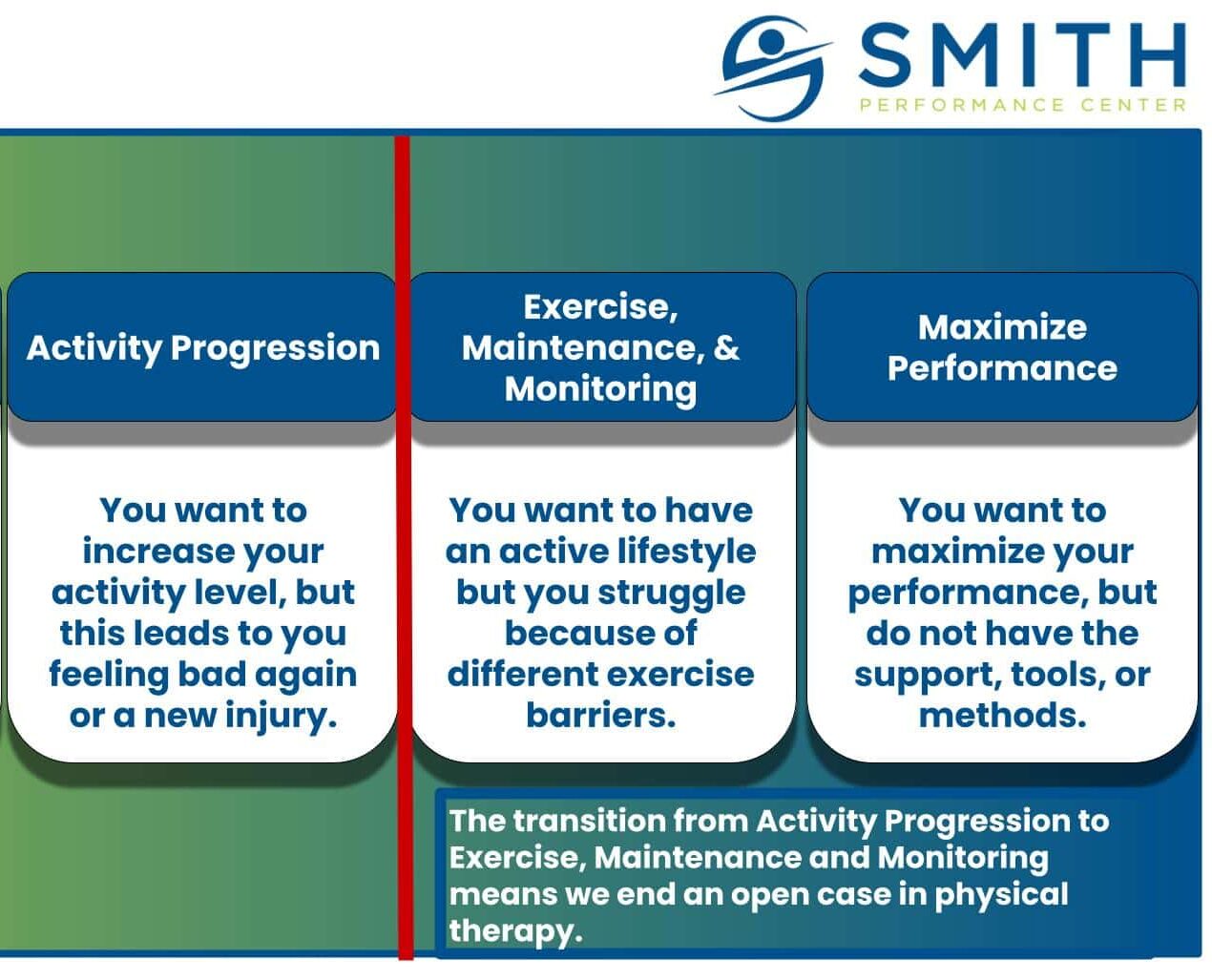
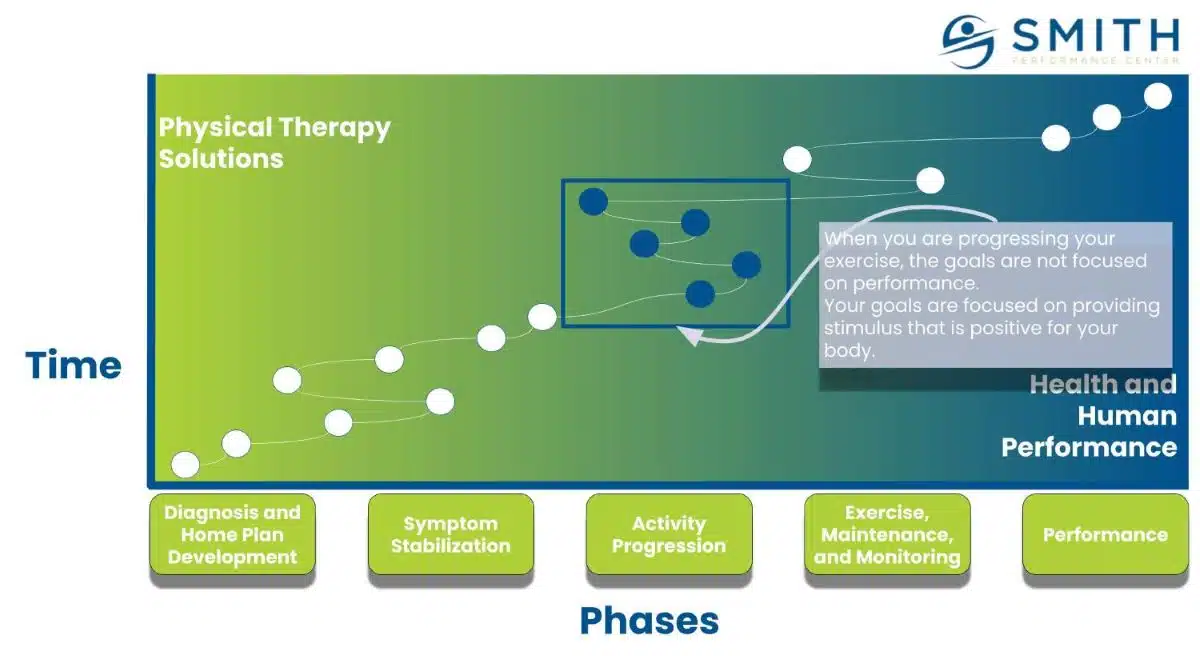
The 4 Types of SPC Supplemental Workouts
The foundation of our programming is the strength workout. Building upon this foundation using a progressive overload approach is essential for long-term strength and fitness gains. Incorporating supplemental workouts can provide variety, target specific muscle groups and movement patterns, develop new skills, and enhance overall fitness and performance. Supplemental workouts can serve various purposes, such as addressing weaknesses, improving mobility, treating recurrent injuries, reducing risk for falls or simply adding diversity to training. They include exercises like mobility drills, corrective exercises, accessory movements, and conditioning work. By integrating supplemental workouts into your programming, you create a more well-rounded and balanced training regimen. This approach not only helps to prevent boredom and plateaus but also allows for continuous improvement and adaptation over time. We want to review the types of supplemental workouts in this article. The 4 types of supplemental workouts We have 4 types of supplemental workouts: We will explain