
How to Avoid “Exercise Hell” (When Exercise Makes You Feel Worse)
When exercise makes you feel worse instead of better, motivation isn’t the problem. Learn why this happens and how to avoid “exercise hell.”
Find related articles and learn more about our process at SPC.

When exercise makes you feel worse instead of better, motivation isn’t the problem. Learn why this happens and how to avoid “exercise hell.”

You’re Doing the Work—So Why Does Your Body Keep Breaking Down? You show up. You put in the effort. Whether it’s running, lifting, group fitness, or weekend hikes, you’re trying to stay active. But despite the commitment, you keep dealing with recurring injury from exercise. Pain shows up, progress stalls, and your body feels more unpredictable than it should. This isn’t about motivation. It’s about biology.The real issue is a mismatch between what you can make yourself do and what your body is built to tolerate. At Smith Performance Center, we call that gap the difference between exercise capacity and tissue capacity the rehab standard—and it’s one of the most overlooked problems in rehab and training. What Is Exercise Capacity? Exercise capacity is your ability to push through effort and accumulate work over time. It’s what most people think of as “fitness.” It includes: Exercise capacity reflects what you’re capable

Confidence is even more important than strength. People come in with doubt and fear of pain. If they don’t believe they can move safely, they won’t move at all. My job is to assess not just their movement, but also their psychological acceptance of movement. The best exercise is the one you can do, so we start small, monitor the response, and slowly build from there

A perfect time to build the exercise habit occurs when you overcome a painful injury. At Smith Performance Center (SPC), this happens during the “activity progression” phase after stabilizing symptoms. Unlike a standard exercise routine, activity progression focuses on managing and improving tissue capacity—your body’s ability to handle physical load without pain or injury. If these terms sound unfamiliar, don’t worry. The following signs indicate you may have skipped the fundamentals of activity progression: Why Delaying Exercise Is a Mistake Many individuals delay exercise until they feel completely better. However, this approach has drawbacks: Your Path at SPC At SPC, we’ve developed a clear plan to help you build fitness while overcoming an injury. Here’s how it works: 1. Your Home Plan: Manage Symptoms and Flare-Ups The biggest hurdle to starting exercise is handling symptom increases. If daily activities cause large spikes in pain, your exercise plan must be carefully
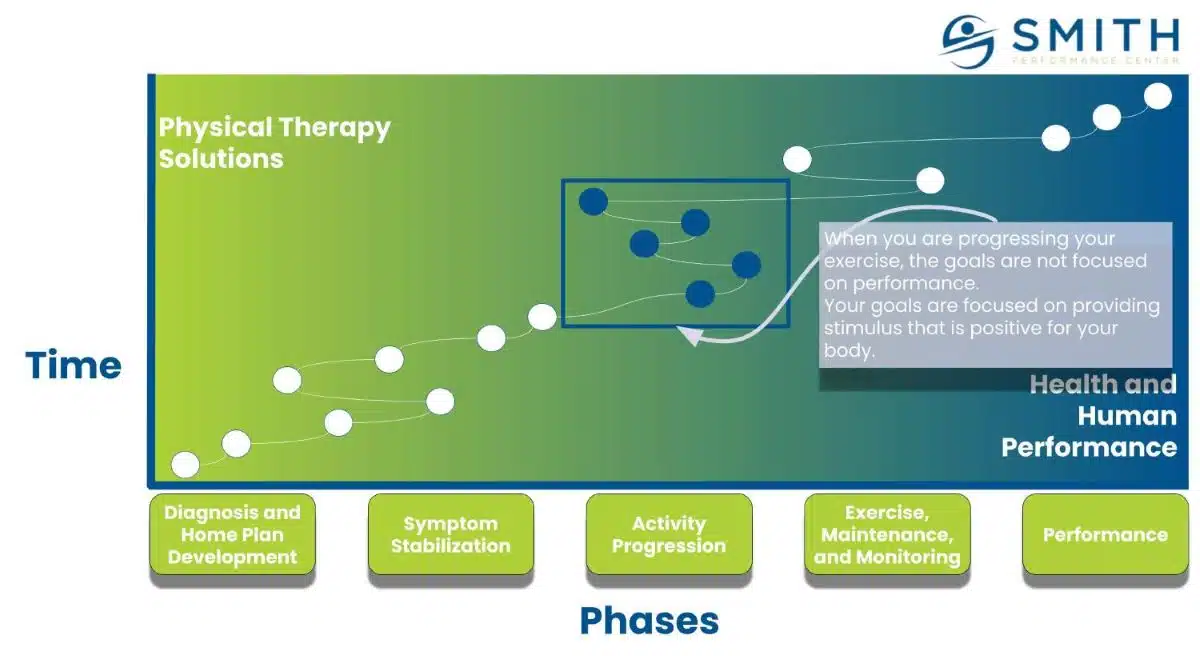
Welcome to the transition zone—phase 3 to phase 4—at Smith Performance Center. This shift marks an important move from rehabilitation to performance. We’re committed to ensuring that our community doesn’t get stuck in a permanent rehab mindset. The switch from rehab mode to peak performance mode can pose challenges, demanding careful consideration and expert guidance. Phase 3 is all about building up tissue capacity, gradually ramping up activity levels, and prioritizing overall well-being. It involves strengthening muscles, alleviating muscle inhibition, closely monitoring responses to increased activity, and addressing any lingering issues stemming from previous inactivity. Essentially, it’s about improving tissue capacity while laying down a solid foundation for what comes next. In contrast, phase 4 signifies a fresh chapter, with a focus on establishing a consistent exercise routine and raising the bar for performance standards. Our goal here isn’t just to ‘move’ but to instill a long-term commitment to fitness

Do you want to get back to exercise but keep on getting hurt? The merry-go-round misery of repetitive injury when exercising is a common complaint at Smith Performance Center. When someone shows up, our physical therapists listen to a series of injuries that seem to occur every time they get into a workout routine. The exerciser finishes rehab and heads back to their respective sport. The first few days go well, but inevitably the same problem comes back. In our clients’ minds, their body has lost the ability to stay healthy. They believe age is driving the problem, or the joints are shot. They think the activity they choose to do is too vigorous and must be replaced. These are not the problem. The cycle of repetitive injury is a strategic mistake. Why Repetitive Injuries Keep Happening When You Exercise We believe in a process called the SPC Phases. A
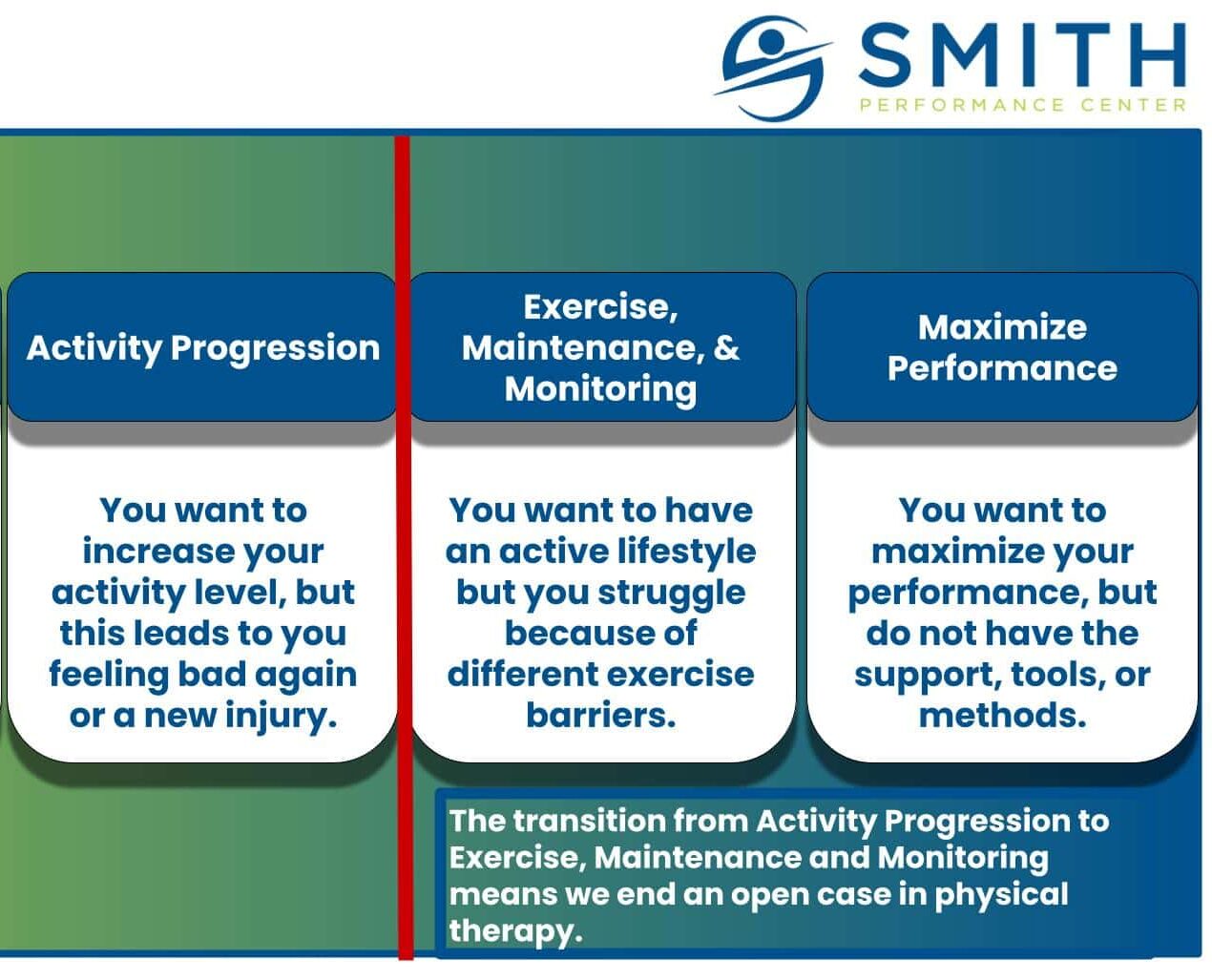
Goal setting is one of the most important, yet tricky aspects of training. Our team believes that goals are secondary to developing habits and systems that you can do day in and day out. We call this an exercise habit and it is a critical aspect of becoming an exerciser. However, goals can help to shape your training, increase motivation, and improve decision-making during the course of workouts. When you are returning from an injury or dealing with a particularly irritating pain, we believe your goal is very specific. You need to exercise without your body feeling terrible. While this sounds obvious, one of the most common training mistakes our coaches see clients make is too much focus on performance while ignoring a recurring injury or pain. If you have pain during your running, biking, lifting, etc., you will not achieve performance goals. We strongly believe there are 4 goals
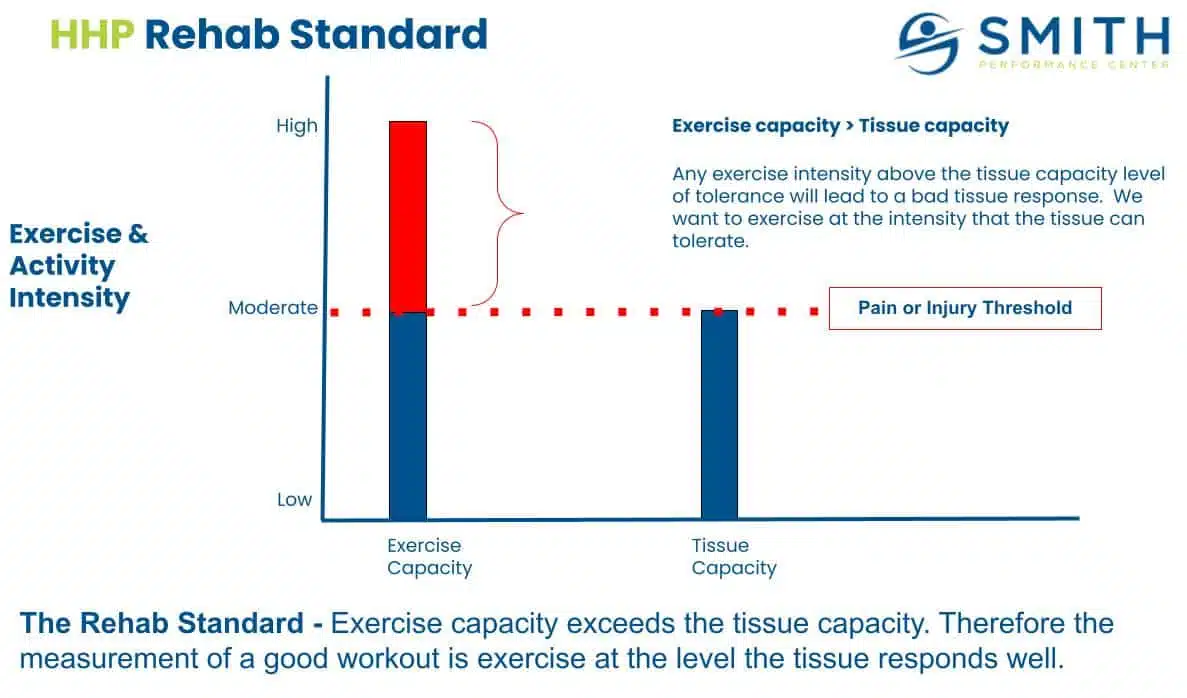
Too many fail in their effort to progress activity after an injury. You arrive at the gym feeling good but later in the day the low back soreness that has been feeling better comes back or the knee pain that seemed to be going away comes back with a vengeance after your second run. The regression happened even when the workout felt easy and pain-free at the time. Why is this happening? Why is this phase of rehab frustrating? It’s due to a fundamental mistake or what we call a violation of the rehab standard, which is training at exercise capacity, not tissue capacity. When individuals make this mistake, they start telling themselves stories like ‘I am getting too old,’ or ‘I guess I need to do something with less impact.’ However, the problem is not due to aging or the fact that the body can return to preinjury levels.

The Rehab Standard is an SPC concept that defines when a client has a higher exercise capacity than tissue capacity. When your tissue capacity is lower than the exercise capacity, the focus of the workout is not how hard you worked out. It is not how much you sweat or how good of a muscle burn you got. The focus is on the healing tissue and that is was not overloaded, irritated, or provoked. A violation of the rehab standard can present as pain after the workout or the next day, even if there was no pain during the workout. The key is to focus on tissue capacity in the exercise selection, intensity, volume and the type of tissue injured. We want to look at this last one, the type of tissue injured, in relation to activity progression following an injury. The 7 Tissues to Consider When Progressing Activity Improving

There are numerous problems facing people in living an active, healthy life, but it can be difficult to articulate the problem that needs to be solved. Let’s look at two people dealing with low back pain. One person bent over this morning to grab a pencil and now cannot stand up straight. The second person developed back pain years ago and stopped doing certain movements because of discomfort. The pain is still present daily and they use a combination of meds, massage, and chiropractic to keep big flares up away. Their problems are different despite both dealing with low back pain. The solutions are very different. The person who just hurt their back needs a diagnosis and a home plan targeting healing strategies and triggers. This may mean more frequent visits and removing anything that makes their symptoms worse. We will likely see this person a few times per week